- by Handson
- August 8, 2025
PROC SQL Tutorial in SAS for Beginners With Example and Interview Questions
What is PROC SQL?
PROC SQL is a powerful procedure in SAS that enables SQL (Structured Query Language) programming. It is used to retrieve, filter, join, and summarize data from one or more datasets, similar to how SQL works in traditional database systems.
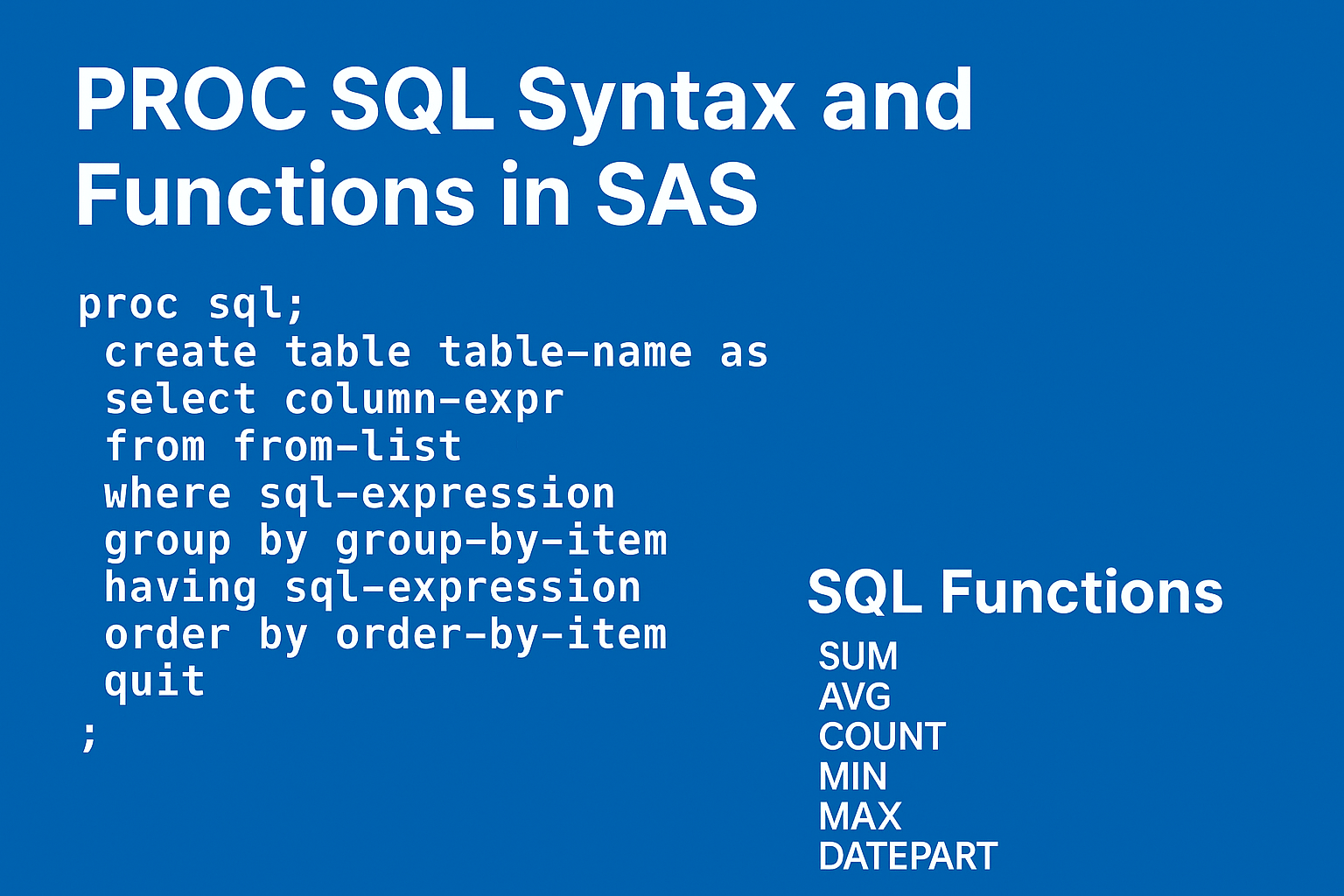
Basic Syntax of PROC SQL
proc sql; select column1, column2 from dataset where condition; quit;
Step-by-Step Example
We will work with a basic dataset containing student information.
Step 1: Create a Sample Dataset
data students; input ID Name $ Gender $ Age Score; datalines; 1 Alice F 22 85 2 Bob M 23 78 3 Clara F 22 92 4 David M 24 88 5 Eva F 23 76 ; run;
This creates a dataset students with five variables.
Step 2: View All Data
proc sql; select * from students; quit;
Explanation: Displays all rows and columns of the dataset.
Step 3: Select Specific Columns
proc sql; select Name, Score from students; quit;
Explanation: Retrieves only the Name and Score columns.
Step 4: Apply Filtering Using WHERE Clause
proc sql; select * from students where Score > 80; quit;
Explanation: Returns students who scored more than 80.
Step 5: Rename Columns with Aliases
proc sql; select Name, Score as Marks from students; quit;
Explanation: Renames the Score column to Marks in the output.
Step 6: Order the Results
proc sql; select * from students order by Score desc; quit;
Explanation: Sorts students by score in descending order.
Step 7: Grouping and Aggregation
proc sql; select Gender, avg(Score) as Avg_Score from students group by Gender; quit;
Explanation: Displays the average score for each gender group.
Step 8: Joining Two Tables
Let’s create another dataset named courses.
data courses; input ID Course $; datalines; 1 Math 2 English 3 Physics 4 Chemistry 5 Biology ; run;
Now perform an inner join on the ID column.
proc sql; select a.Name, b.Course from students as a inner join courses as b on a.ID = b.ID; quit;
Explanation: Matches records from students and courses on the ID field.
Interview Questions and Answers on PROC SQL
1. What is the use of PROC SQL in SAS?
Answer:
PROC SQL allows you to manipulate and retrieve data using SQL syntax within SAS. It supports operations such as selection, filtering, aggregation, joining datasets, and subqueries.
2. How is PROC SQL different from the DATA step?
Answer:
-
The DATA step processes data row by row and is more suitable for iterative operations.
-
PROC SQL works on a set-based approach and is often more concise.
-
PROC SQL is preferred for joining tables and performing group-level calculations, while the DATA step gives more control over individual record-level manipulations.
3. Can PROC SQL be used to create new variables?
Answer:
Yes, you can create new variables using calculated expressions within SELECT statements. For example:
proc sql; select Name, Score, Score + 5 as Adjusted_Score from students; quit;
4. How do you remove duplicates in PROC SQL?
Answer:
Use the DISTINCT keyword.
proc sql; select distinct Gender from students; quit;
5. What is the default join type in PROC SQL?
Answer:
If not specified, there is no implicit join. You must explicitly define the join type (e.g., INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN). Unlike some SQL dialects, SAS does not assume a join by listing multiple tables in the FROM clause without a JOIN condition.
6. Can PROC SQL create new datasets?
Answer:
Yes. Use the CREATE TABLE statement.
proc sql; create table top_students as select * from students where Score > 85; quit;







